A Modern Guide to Managing Source Code
Managing your source code is all about keeping track of the changes made to your software's DNA—the code itself. It's way more than just saving files. Think of it as the foundational practice for collaborative development, making sure your team can work together without tripping over each other or losing critical history.
The Blueprint for Collaborative Development
Imagine trying to build a modern skyscraper without a central blueprint. You'd have different crews working in isolation, walls wouldn't line up, and the whole project would descend into chaos. That's exactly what software development looks like without a smart way to manage source code. This guide is that essential blueprint.

Good source code management makes collaboration feel effortless. It tracks every single change and prevents the kind of costly mistakes that can completely derail a project. Just dumping code into a shared folder? That's a recipe for disaster, leading to version conflicts, lost work, and zero accountability. This is where tools like Git come in, providing the structure and safety nets your team needs to build with confidence.
Why Is Source Code Management So Important?
Let's be clear: properly managing source code isn't optional in modern software engineering. It's what moves teams from disorganized chaos to structured, productive work by creating a single source of truth for the entire project. This organized approach is also a perfect fit with an Agile Development Methodology, which thrives on the same kind of iterative, trackable progress.
The numbers back this up, too. The global market for Source Code Management (SCM) software sits somewhere between USD 1.1 billion and USD 2.9 billion in 2024. It's expected to grow to between USD 1.6 billion and USD 5.8 billion by 2030, which shows just how much companies are investing in getting this right.
At its heart, managing source code isn't just a technical chore—it's a communication tool. Each commit, branch, and pull request tells a story about the project's evolution, its challenges, and its successes. It creates a living history that empowers every developer on the team.
This approach is the key to creating a unified, high-velocity development environment. Once you have your version control locked down, the next logical step is integrating it with your project management tools. If your team is on popular platforms, learning how to link Jira to GitHub can make your workflow even smoother.
Understanding How Version Control Works
At the heart of all modern source code management is a simple but powerful idea: version control.
Think of your project's code repository as a meticulously kept history book. This isn't just a backup; it’s a living document that chronicles the entire life of your software, from the very first line of code to the latest feature release.
Every time a developer saves their work, they create a "commit." A commit is like a new, timestamped entry in that history book. It's a complete snapshot of the project at that exact moment, capturing what changed, who made the change, and—most importantly—why they made it. This creates an unchangeable, step-by-step record of the project's evolution.
Centralized vs. Distributed Systems
Not all version control systems (VCS) manage this history book in the same way. The main difference comes down to where the "master copy" of the book is stored. Understanding this split is key to understanding modern development.
Early systems were almost all centralized.
- Centralized Version Control (CVCS): In this classic model, one central server holds the single, authoritative copy of the project's history. Developers "check out" the files they need, make their changes, and then "commit" them directly back to that server. Tools like Subversion (SVN) and Perforce still work this way.
The approach is simple, but it has one massive flaw: that central server is a single point of failure. If it goes down, nobody can collaborate. If its history gets corrupted, you could lose everything.
The real game-changer in source code management was the shift to a decentralized, or distributed, model. It solved the single-point-of-failure problem and unlocked new levels of speed and flexibility for developers.
This newer model gave rise to the tools that absolutely dominate software development today.
The Power of a Distributed Approach
A Distributed Version Control System (DVCS), like the industry-standard Git, flips the model on its head. Instead of just checking out a few files, every developer "clones" the entire repository—including its full history—onto their local machine.
That’s right. Every team member has a complete, fully functional backup of the project. This distributed nature offers some huge advantages:
- Offline Capability: Developers can commit changes, dig through project history, and even create new branches without needing an internet connection.
- Blazing Speed: Since most operations happen locally instead of over a network, actions like committing and viewing history are nearly instantaneous.
- Better Collaboration: This model enables much more complex workflows, as developers can pull changes directly from each other's local repositories without ever touching a central server.
This fundamental shift—from one master copy to many complete copies—is what gives modern tools like Git their incredible resilience and power. It's the foundation for managing code effectively in teams of any size.
Choosing The Right Branching Strategy
Once you've got the hang of version control, the next big step is figuring out how your team will actually make changes to the code. Think of your commit history as the official timeline of your project. If that's the case, branches are the alternate realities—parallel universes where developers can safely build new features, squash bugs, or just experiment without blowing up the main codebase.
This isolation is everything. Imagine a world without branches: every developer pushes their changes directly to the stable, production-ready code. It would be absolute chaos. One person's unfinished feature could break the entire application for everyone else. Branches prevent this nightmare by giving each task its own dedicated workspace.
A branching strategy is just a set of rules for managing this process. The right one brings order to your workflow, makes collaboration feel effortless, and keeps your team aligned with your release schedule.
Gitflow: A Highly Structured Model
If you're working on a project with a formal, scheduled release cycle—like a mobile app with distinct versions such as v1.0, v1.1, and v2.0—then GitFlow is your best friend. It’s a beautifully structured, if somewhat complex, model that uses a system of long-lived and short-lived branches to keep things organized.
The main players in GitFlow are:
main: This is sacred ground. It holds the official, production-ready code. It should always be stable.develop: The integration branch where all new features come together. Think of it as the staging area for the next release.- Feature Branches: Spun off from
develop, this is where developers build new things. When a feature is done, it gets merged back intodevelop. - Release Branches: When
developis ready for a new release, areleasebranch is created. This is where you'll handle last-minute bug fixes and final prep work. - Hotfix Branches: Created directly from
mainto fix urgent, production-breaking bugs. They get merged back into bothmainanddevelopto keep everything in sync.
This methodical approach is fantastic for maintaining multiple versions of a product at once. But for teams that push code multiple times a day, its ceremony can feel like overkill.
Github Flow: A Simpler Approach For Continuous Delivery
For teams that live and breathe continuous delivery—shipping updates as soon as they're ready—GitFlow's structure is just too slow. That's where a lean model like GitHub Flow comes in. It's built on a single, powerful idea: the main branch is always deployable.
The workflow is beautifully simple:
- Create a descriptive branch off
mainfor any new task (e.g.,fix-user-login-bug). - Push your commits to that branch as you work.
- Open a pull request when you're ready for feedback and review.
- Once it's approved, merge it into
main. - Deploy the updated
mainbranch right away.
GitHub Flow’s simplicity makes it incredibly fast and efficient. It eliminates the complexity of multiple long-lived branches, making it a perfect fit for web applications and services where rapid iteration is key.
The following diagram illustrates the two main types of version control systems where these strategies are used.
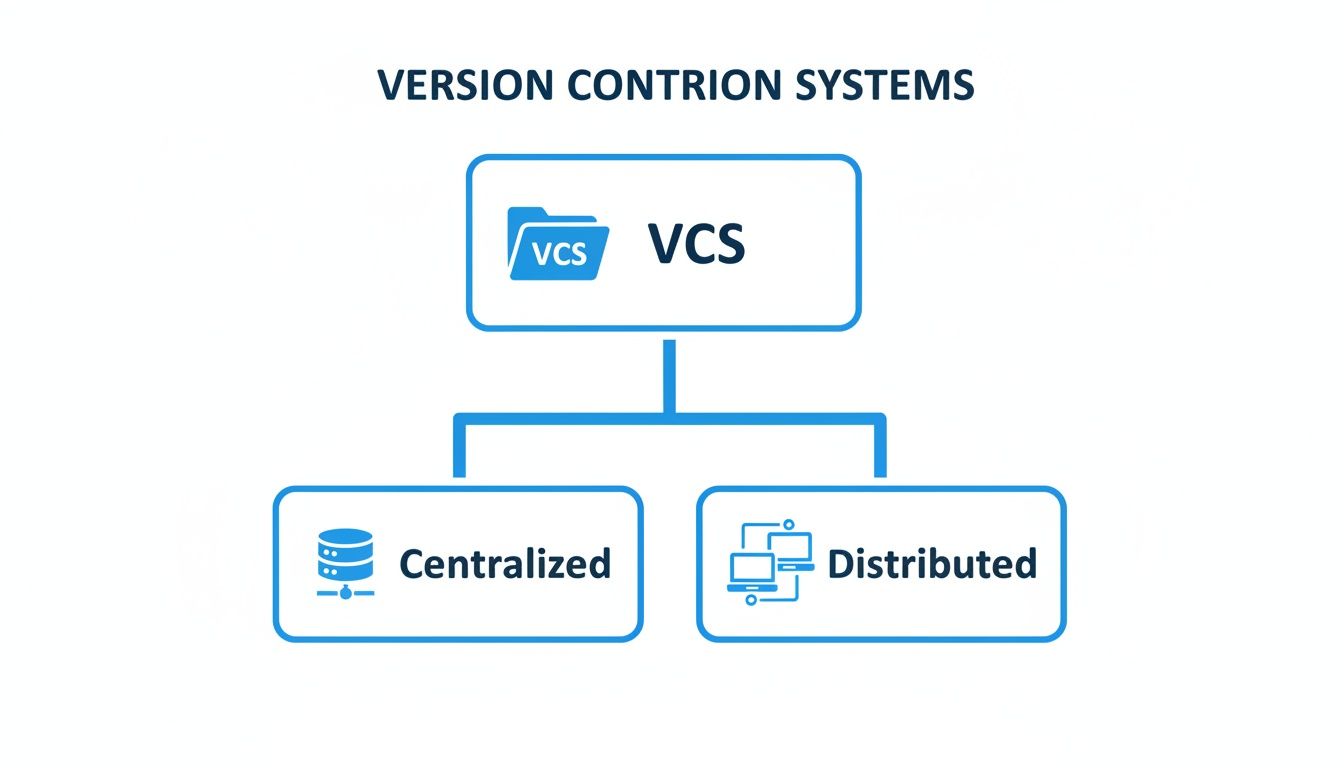
This visual shows the core difference between centralized systems, where one server holds all the power, and distributed systems like Git, which enable these flexible branching models by giving every developer a complete copy of the repository.
Trunk-Based Development: The Ultimate In Speed
Trunk-Based Development (TBD) takes simplicity to its logical extreme. Here, developers work in tiny batches and merge their code directly into a single main branch (the "trunk") several times a day. Feature branches are either avoided completely or are so short-lived—lasting maybe a few hours—that they barely count.
This strategy is not for the faint of heart. It relies heavily on a rock-solid automated testing suite and a powerful CI/CD pipeline to keep the trunk stable. TBD is the go-to model for elite teams at places like Google and Meta because it practically eliminates merge conflicts and creates an insanely fast feedback loop. The secret sauce? Feature flags, which let you merge unfinished code safely by hiding it from users until it’s ready.
Comparison of Popular Branching Strategies
Choosing the right strategy isn't about picking the "best" one, but the best one for your team. Each model comes with its own trade-offs in complexity, speed, and structure.
| Strategy | Best For | Complexity | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| GitFlow | Projects with scheduled, versioned releases (e.g., mobile apps). | High | Strict separation of development, release, and production code. |
| GitHub Flow | Teams practicing continuous delivery and rapid iteration (e.g., web apps). | Low | The main branch is always deployable. |
| Trunk-Based Development | High-performing teams with robust CI/CD and automated testing. | Very Low | All developers commit to a single main branch. |
Ultimately, the goal is to find a workflow that supports your team’s rhythm. GitFlow provides stability for planned releases, GitHub Flow offers speed for continuous deployment, and Trunk-Based Development delivers the ultimate velocity for teams with mature DevOps practices.
Automating Quality with Code Reviews and CI/CD
Just getting your code to work is only the first step. The real challenge in managing source code is ensuring its quality, security, and maintainability over the long haul. This is where two practices are absolutely critical: collaborative code reviews and automated CI/CD pipelines. When you put them together, you create a powerful quality net that catches problems early and keeps your codebase from turning into a mess.

Code reviews, usually handled through pull requests (or merge requests, depending on your platform), shouldn't feel like a chore or a gatekeeping exercise. Think of them as a collaborative learning process—a structured way for developers to share knowledge, offer improvements, and make sure new code actually fits with the team's established standards.
Best Practices for Effective Code Reviews
To make your reviews count, you need to focus on constructive communication and clear goals. The point is to make the code better, not to criticize the person who wrote it.
- Keep Pull Requests Small: Nobody wants to review a single, monstrous 500-line change. It's exhausting and mistakes get missed. Small, focused PRs are way easier to understand, review properly, and merge without breaking things.
- Provide Clear, Actionable Feedback: Instead of just saying "this is confusing," try something like, "Could we rename this variable to
userIsAuthenticated? It would make the logic clearer." Be specific about what should change and, more importantly, why. - Automate Style Checks: Use tools like linters and code formatters. Let the machines argue about comma placement and indentation. This frees up human reviewers to focus on what really matters: the logic, the architecture, and the bigger picture.
An effective code review culture transforms a team. It moves from a mindset of "Is this code correct?" to "Is this code the best it can be for our team and our product?" This shift fosters collective ownership and elevates the quality of the entire codebase.
Supercharging Your Workflow with CI/CD
While human code reviews are essential for collaboration and knowledge sharing, automation is what gives you speed and consistency. This is where CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery) pipelines come in. A CI/CD pipeline is like an automated assistant that jumps into action every time a developer submits a change.
This automated workflow is the bedrock of modern software development. The market trends reflect this reality. North America, for example, is the dominant force in the global source code management software market, holding about 35.67% of the market share in 2023. The United States alone is expected to grab around 22.4% of the global SCM market by 2025, thanks to huge investments in the kind of tech infrastructure that powers practices like CI/CD.
A standard CI pipeline will automatically handle several key tasks:
- Builds the Application: First, it compiles the code to make sure there are no glaring syntax errors.
- Runs Automated Tests: It then runs your entire test suite—unit tests, integration tests, end-to-end tests—to catch any regressions or new bugs instantly.
- Performs Static Analysis: The pipeline can also scan the code for common security vulnerabilities, performance red flags, and style guide violations.
This whole process gives developers fast, objective feedback in minutes, letting them fix issues before a human reviewer even lays eyes on the code. Continuous Delivery takes it a step further by automatically deploying the code to a staging or production environment once it passes all the checks and gets merged.
Of course, once your CI/CD pipeline confirms you have a solid, deployable app, you still have to get it to your users. For mobile developers, that means navigating the app store submission gauntlet. Thankfully, there are great guides on things like how to publish your app to Google Play that can make that final step a lot less painful.
By combining the human insight from code reviews with the relentless consistency of CI/CD, you build a powerful, automated quality engine that makes managing your source code both efficient and reliable.
Embedding Security into Your Workflow
Let’s be honest: managing source code is about more than just tracking changes and merging branches. Your code is one of your most valuable, sensitive assets. That means you have to treat it that way, weaving security directly into how you build things from day one.
This whole idea is often called DevSecOps. It’s a shift away from treating security as a final checklist item before you ship. Instead, it becomes a shared responsibility that starts with the very first line of code written.
Protecting your code isn't just about locking down your repository, either. The real dangers are often hiding in plain sight inside the code itself—a subtle vulnerability here, an insecure open-source library there, or—the classic—a hardcoded password just waiting to be discovered. In today's world, a proactive security posture isn't just a good idea; it's non-negotiable.
Finding Flaws with Automated Scanning
The only realistic way to keep up is to automate. You need tools that can find problems faster than a human ever could. Two types are absolutely essential:
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST): Think of a SAST tool as a spell-checker, but for security holes. It scans your raw source code—without ever running it—to spot common vulnerability patterns. Things like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and sloppy error handling that could leak sensitive information.
- Software Composition Analysis (SCA): Let's face it, nobody builds applications from scratch anymore. We all stand on the shoulders of open-source libraries and frameworks. SCA tools act like a meticulous librarian for your dependencies. They scan every third-party package you use and check them against a massive database of known vulnerabilities.
When you plug these scanners directly into your CI/CD pipeline, they create an automated safety net. If a developer accidentally pushes some risky code or pulls in an outdated library with a known flaw, the build fails immediately. The problem gets flagged before it ever has a chance to get merged into your main branch.
The Critical Role of Secrets Management
One of the single most common—and most dangerous—security blunders is hardcoding secrets. We’re talking API keys, database passwords, and authentication tokens written directly into a config file or the source code itself. The moment that code gets pushed to a repository, those secrets are exposed to anyone with access. It's a massive, gaping security hole.
Secrets management is the simple but powerful practice of ripping sensitive information out of your code and storing it somewhere safe, like a dedicated vault. This guarantees credentials are never, ever committed to your project's history.
Instead of having a password sitting in a file, your application fetches it from the secure vault when it starts up. This is a game-changer for a few reasons:
- It kills accidental exposure: Your Git history stays clean. Even if your entire repository is compromised, your most critical credentials remain locked away and safe.
- It makes rotating credentials painless: Need to change a password or an API key? You update it in one place—the vault. No code changes, no redeployments, no hassle.
- It gives you a crystal-clear audit trail: Secure vaults log every single time a secret is accessed. This is a lifesaver for security audits and proving compliance with standards like SOC 2 or HIPAA.
By combining automated SAST and SCA scanning with disciplined secrets management, you fundamentally change your team’s relationship with security. It stops being an annoying afterthought and becomes a core part of your workflow. This DevSecOps mindset doesn't just prevent breaches; it builds a more resilient and trustworthy codebase from the ground up.
So, How Do We Handle All This AI-Generated Code?
AI coding assistants are completely changing the game. Tools like GitHub Copilot can spit out entire functions in the blink of an eye, which feels like a massive productivity boost. But this speed comes with a price, and if you don't have a plan, you're walking straight into a minefield.
Just blindly accepting every suggestion from an AI is a recipe for disaster.
On the surface, the code might look fine. It might even run. But lurking underneath, you could be introducing subtle security holes, performance killers, or just plain weird logic bugs. We're seeing a lot of what people are calling "code hallucinations"—code that looks perfectly reasonable but is fundamentally broken or wildly inefficient.
And it's not just a technical problem. These AI models were trained on mountains of public code from across the internet. What happens when it generates a snippet that carries a restrictive open-source license? If you drop that into your proprietary product without realizing it, you've just created a massive legal headache for your company down the road.
You Need a Governance Framework
To get all the benefits of AI without the baggage, your team needs a clear set of rules. The starting point is simple but non-negotiable: treat AI-generated code with the exact same skepticism as code written by a junior developer on their first day. It's not magic. It's a first draft that absolutely requires a second pair of eyes.
A developer's core responsibility doesn't change just because an AI is involved. The job is still to ship high-quality, secure, and maintainable code. The AI is an assistant, not the expert—the developer is still the one who owns the quality.
A solid framework needs a few key pillars to keep everyone on the same page and prevent sloppy code from slipping through. Laying out these ground rules is the first step to making AI a truly useful part of your workflow.
Practical Policies That Actually Work
Putting effective policies in place means mixing good old-fashioned human oversight with smart automation. Your team's guidelines need to be crystal clear about how AI-generated code is handled.
Here are a few rules to get you started:
- Human Review is Mandatory: Every single line of AI-generated code gets reviewed by a human. I don't care if it looks trivial. Someone else needs to check it for logic, security flaws, and whether it even matches your team's style guide. No exceptions.
- Check for Licenses and Origins: Train your developers to be suspicious. If a complex block of code appears out of nowhere and looks a little too perfect, it might be lifted from a source with an incompatible license.
- Automate Checks Inside the IDE: The best way to enforce these rules is to catch problems before the code is even committed. Modern tools can plug right into the developer's editor, giving real-time feedback on AI code against your security policies and team standards. It can even check if the code actually matches the developer's original prompt.
Think of these practices as a safety net. For a deeper look at the kinds of problems that can pop up, check out our guide on common AI-generated code issues. By combining clear policies with automated guardrails, you can let your team use AI to boost productivity without sacrificing the quality, security, and integrity of your codebase.
Got Questions About Source Code Management?
As engineering teams start using more sophisticated ways to handle their code, a few questions always seem to pop up. Let's clear the air with some straight-up answers to help you get a handle on the tools and ideas that drive modern software development.
What's the Difference Between Git and GitHub?
This is easily the most common point of confusion for anyone new to the game. The simplest way I've found to explain it is this: Git is the engine, and GitHub is the car.
Git is the powerful, open-source version control system that actually runs on your local machine. It’s the tool tracking every change, creating branches, and managing your project's entire history. You can use Git all day long without ever opening a web browser.
GitHub, on the other hand, is a web-based service built on top of Git. It gives your team a central, cloud-based place to store all your code repositories. But more importantly, it adds a whole layer of collaboration tools that Git alone doesn't have—things like pull requests for code reviews, issue tracking for project management, and slick automated workflows with GitHub Actions. You can use Git without GitHub, but you can't use GitHub without Git.
How Does Version Control Help a Solo Developer?
Even if you're a team of one, version control is an absolute superpower. Think of it as the ultimate safety net. It gives you the freedom to go wild and experiment with new features in a separate branch, all without any risk of torching your stable, working code. It’s a project-wide "undo" button that can save you from those "what did I just do?" moments.
For a solo developer, commit messages become a personal development log. They document your thought process, explaining why you made a particular change. This is incredibly valuable when you come back to that code six months later with zero memory of what you were thinking.
Ultimately, it brings structure, a clear history, and a whole lot of peace of mind to your personal projects. It just makes you a more disciplined and effective developer, period.
What Makes a Good Commit Message?
A good commit message tells a clear story for your future self and your teammates. Vague notes like "fixed bug" or "updated code" are completely useless. The best practice is a dead-simple, two-part structure.
First, write a short, punchy subject line that summarizes the change in 50 characters or less. Treat it like an email subject line—get straight to the point.
- Good:
Add user authentication endpoint - Bad:
made some changes to the user file
Second, if you need to add more color, just add a blank line and then write a more detailed body. This is where you explain the "why" behind the change, not just the "what." When you do this, your Git history transforms from a simple log into searchable, invaluable project documentation.
Stop letting code hallucinations and security risks slow you down. kluster.ai delivers real-time, in-IDE code reviews for AI-generated code, catching issues before they're ever committed. Enforce your team's standards automatically and merge PRs in minutes, not days. Start for free at kluster.ai and make every commit production-ready.