A Developer's Guide to Link Jira to GitHub
Connecting Jira to GitHub is one of those small changes that has a massive impact. It creates a single, reliable source of truth for your entire development process and lets developers update project status right from their code commits. No more manual ticket updates, and way less context switching.
This integration bridges the gap between project management in Jira and the actual coding happening in GitHub, smoothing out the whole workflow.
Why Bother Connecting Jira and GitHub?
Before we jump into the "how," let's talk about the "why." Hooking these two platforms together isn't just about convenience; it's a foundational move for any team serious about building a transparent and efficient development lifecycle. It’s the simplest way to end the constant back-and-forth between project managers asking for status updates and developers who just want to stay focused on code.
Establish a Single Source of Truth
When you link Jira to GitHub, you create an unbroken chain of information. A project manager can pull up a Jira ticket and immediately see every single related branch, commit, and pull request.
That means no more digging through Slack messages or email chains to figure out what’s going on with a task. Every piece of development work is directly tied back to the project plan, giving everyone involved a clear, up-to-the-minute picture.
This unified view is a game-changer for reducing misunderstandings. When everyone is working from the same information, you can stop scope creep in its tracks and keep projects running on schedule.
Boost Developer Productivity and Focus
Developers do their best work when they can stay in their coding environment. Constantly jumping between an IDE, GitHub, and then back to Jira to update a ticket is a massive drain on mental energy and kills momentum.
With a solid integration, developers can use smart commits to transition Jira issues, log time, or add comments without ever leaving their terminal. It sounds like a small thing, but it has a huge impact on daily productivity and aligns perfectly with modern software development best practices. For teams truly interested in mastering the agile product development process, this kind of integration is non-negotiable—it enables smoother sprints and better project oversight.
Give Stakeholders Unmatched Visibility
For stakeholders, product owners, and other non-technical folks, this integration offers a crystal-clear window into the development pipeline. They can track an issue from its creation as a user story all the way to a merged pull request running in production.
This level of transparency builds trust and makes forecasting and planning way more accurate. Instead of waiting for the weekly status meeting, stakeholders can get real-time insights whenever they need them. This leads to more informed decisions and a much healthier rhythm for the entire project.
Choosing The Right Integration Method For Your Team
Connecting Jira and GitHub isn't a one-size-fits-all decision. The best path for your team really hinges on a few key things: your team's size, how much technical firepower you have, and the nitty-gritty details of your workflow. Before we jump into the options, it's worth understanding the bigger picture of What is System Integration, because linking these two powerhouses is a perfect real-world example.
For most teams, the simplest and most effective route is the official GitHub for Jira app straight from the Atlassian Marketplace. It’s built for a no-fuss setup, gives you a ton of functionality right out of the box, and Atlassian keeps it updated. This approach provides that rich context everyone wants—seeing related branches, commits, and pull request statuses directly inside your Jira issues.
But sometimes, a pre-built app just doesn’t cut it.
When To Consider a Custom Approach
If your workflow has unique triggers or you need to sync custom fields between the two platforms, you’ll probably need a more tailored solution. This is where rolling your own integration using webhooks and APIs comes into play. It offers complete flexibility but requires a developer to build and maintain it.
For instance, you could set up a webhook that kicks off a specific job in your CI/CD tool the moment a comment is posted on a pull request. That's a level of granular control the official app might not offer.
For massive organizations with a complex web of tools, there's another option: an Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS). These platforms are like a central hub connecting not just Jira and GitHub, but also tools like Salesforce, Slack, or Zendesk. This is the way to go when you need to orchestrate complex workflows that span multiple systems and departments.
Key Takeaway: Start with the official Marketplace app. Seriously. It covers over 80% of what most teams need. Only dive into custom webhooks or an iPaaS if you hit a specific wall or have enterprise-level needs that go way beyond simple dev visibility.
This flowchart lays out the core decision: connect the platforms to get a massive efficiency boost, or keep them separate and deal with the consequences.
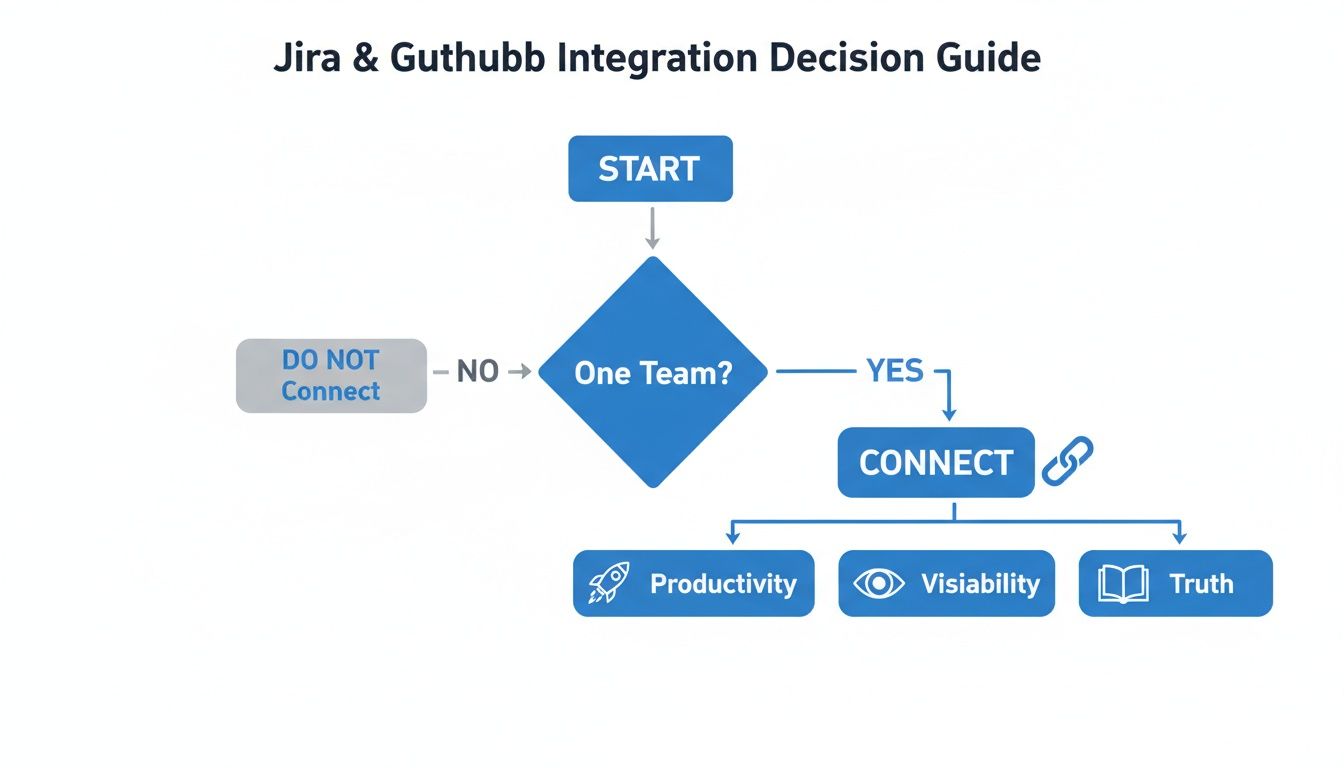
As the visual makes clear, for the vast majority of development teams, the payoff—better productivity, total visibility, and a single source of truth—is well worth the effort of connecting the tools.
Jira and GitHub Integration Methods Compared
To help you decide, here’s a quick breakdown of the common methods, their strengths, and where they shine.
| Integration Method | Best For | Ease of Setup | Customization Level | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marketplace App | Most teams, from startups to enterprises, who need core visibility into dev work. | Easy | Low | Out-of-the-box visibility into branches, commits, PRs, and builds directly in Jira. |
| Webhooks & APIs | Teams with specific, unique workflow needs and available development resources. | Difficult | High | Trigger custom actions in other systems based on very specific GitHub events. |
| iPaaS Platforms | Large organizations managing complex, multi-system workflows across the company. | Medium | Medium-High | A central hub to orchestrate data flow between many different business applications. |
| Smart Commits | Developers who want a quick, lightweight way to link code to issues without leaving their terminal. | Easy | Low | Update Jira issues (comment, log time, transition) directly from commit messages. |
Ultimately, choosing the right method upfront ensures you get the most value from linking Jira to GitHub and that the integration actually supports how your team works.
How to Link Jira and GitHub with the Official App
For most teams, the fastest and most reliable way to connect Jira and GitHub is by grabbing the official GitHub for Jira app from the Atlassian Marketplace. It's the officially supported route, a breeze to set up, and it’s packed with the features you actually need to see what’s happening in your codebase right from your project board.

Honestly, this method beats building something custom any day of the week. You get immediate access to development context inside your Jira issues without writing a single line of code. Let’s walk through getting this powerful connection up and running.
Finding and Installing the App
First things first, you'll need to head to the Atlassian Marketplace, which you can do right from your Jira instance. If you're a Jira admin, just click the Settings gear icon and select Apps. From there, a quick search for "GitHub for Jira" will bring up the official application.
Go ahead and click Get app. The installation is usually pretty quick and happens in the background. In just a few moments, the app will be added to your Jira instance, and you'll be ready to hook it up to your GitHub organization.
Connecting Your GitHub Organization
With the app installed, look for a new "GitHub" option under your Jira settings or a "Get Started" button on the app management screen. Clicking this kicks off the authentication process. This is where you’ll grant the app access to your GitHub organization.
Here's the most common snag people hit: the person setting this up must have owner-level permissions in the GitHub organization. I can't stress this enough. The app needs these elevated permissions to install the webhooks that listen for events like commits and pull requests. Without them, the connection will fail.
You’ll be asked which repositories to connect, but you don’t have to sync everything at once. I always recommend starting with a single, active project repository to test the connection. This lets you kick the tires before rolling it out to your entire organization.
This controlled approach helps you verify that everything is working as expected without creating a ton of noise. You can always add more repositories later on.
Final Configuration and Verification
Once you’ve authenticated and picked your repositories, the initial sync will begin. The app will start pulling in recent development data, linking it to your existing Jira issue keys.
To make sure the integration is really working, run a quick test:
- In a connected repository, create a new branch using a valid Jira issue key (e.g.,
feature/PROJ-123-new-login-flow). - Push a commit with the issue key in the message (e.g.,
git commit -m "PROJ-123: Initial commit for login page"). - Open ticket
PROJ-123back in Jira. You should now see a new development panel showing the branch and commit information. If you see that, you're golden.
Since 2025, connecting GitHub Cloud or GitHub Enterprise Cloud to Jira Cloud with this app has become the gold standard for software teams. It’s the simplest way to track branches, commits, and pull requests directly within Jira, bridging the gap between your development and project management workflows. You can learn more about how this integration works on Atlassian's support page.
Okay, you've got the basic connection humming along. Now it's time to make this integration really work for you, moving beyond just seeing GitHub activity in Jira and into genuine automation. This is where you can save your team from the tedious busywork that drains their focus.
The two best tools for this job are Smart Commits and Jira Automation rules. Let's dig in.

Smart Commits are basically special commands you bake right into your commit messages. They let developers update Jira issues—change statuses, add comments, log time—without ever leaving their terminal. It's a small change that makes a huge difference in the day-to-day grind.
Think about it. A single commit message like git commit -m "PROJ-451 #in-progress #comment Fixing the login bug." can link the commit to the ticket, move that ticket to "In Progress," and drop a comment on it. That's efficiency.
Mastering Smart Commit Syntax
Getting the hang of Smart Commits is pretty straightforward once you see the pattern. You just need the Jira issue key, followed by a command starting with a hash (#).
Here are the most useful ones you can start using immediately:
- #comment Slaps a comment onto the specified Jira issue.
- #time Logs work on a ticket (e.g.,
#time 1w 2d 3h 45m). - #transition Moves an issue to another status in your workflow (like
#in-reviewor#done).
You can even string multiple commands together in one go. Something like PROJ-789 #time 2h 30m #comment Final adjustments complete. #done will log your time, add that comment, and close the ticket all at once.
Pro Tip: Create a cheat sheet for your team with the exact names of your project's workflow statuses (e.g., 'Code Review', 'Ready for QA'). This simple step prevents failed commands from typos and gets everyone on the same page.
Building Powerful Jira Automation Rules
While Smart Commits are driven by developers, Jira Automation is where you, as a manager or lead, can build rules that react to GitHub events on their own. This is how you standardize your process and make sure your Jira board is always an accurate reflection of reality.
A great place to start is with a rule that moves an issue when a pull request is opened. Imagine a developer creates a PR for their branch. Without anyone having to lift a finger in Jira, the ticket automatically slides from "In Progress" to "In Review." That direct link between coding activity and project status is exactly what this integration is all about.
Here are a few other powerful automations you can set up in just a few minutes:
- When a PR is opened -> Transition the related issue to "In Review."
- When a PR is merged -> Add a comment like "Merged and ready for deployment" and move the issue to "Done."
- When a build fails in GitHub Actions -> Fire off a comment to the Jira issue and assign it back to the developer.
These rules create a self-updating system, so your project status is never stale. For any team doing continuous integration, these automations are non-negotiable for clear communication and following the best practices for code review.
Exploring Advanced Third-Party Integration Solutions
The official GitHub for Jira app is a fantastic starting point and covers the essentials for most teams. But what happens when "the essentials" aren't enough? For large organizations juggling complex workflows across multiple departments and a sprawling software stack, the native app can feel a bit limiting.
When you need more than just a window into your code, it's time to look at specialized third-party connectors and what the industry calls Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) solutions.

These tools are built for the heavy lifting that the standard integration just wasn't designed for. They go way beyond simply displaying data, offering deep, bidirectional syncing. In practice, this means an update to a custom field in Jira could automatically add a specific label in GitHub—and an action in GitHub could trigger a change right back in Jira.
When to Invest in a Specialized Connector
So, how do you know it's time to upgrade? It usually comes down to hitting a wall with the standard setup. If your team is wrestling with any of the following scenarios, a dedicated connector might be the right call.
- You Need True Bidirectional Syncing: Your workflow demands that changes in one system are perfectly mirrored in the other, not just shown as a reference. Think bigger: closing a Jira epic automatically archives the corresponding GitHub repo.
- Your Field Mapping is Complex: You need to sync custom Jira fields with GitHub labels, milestones, or even specific text inside a pull request description. The native app just doesn't offer that level of granularity.
- Workflows Span Multiple Platforms: Your process involves more than just Jira and GitHub. Maybe you need to kick off a deployment in your CI/CD pipeline or update a Salesforce record when a PR is merged.
These connectors are designed for situations where you need to link Jira to GitHub as one crucial step in a much larger, automated chain of events. They act as a powerful middle layer, giving you pinpoint control over how information flows between your tools.
This move toward more deeply connected systems is why the market for these tools is exploding. Organizations are realizing the power of tightly coupling their engineering work with their business operations. This trend is a huge driver behind the growth of the iPaaS market, which is projected to jump from USD 17.55 billion in 2025 to a staggering USD 79.38 billion by 2030. You can dig deeper into the growth of Jira-GitHub integration tools to see just how fast this space is evolving.
The decision to pay for a third-party tool often boils down to one simple question: Is the time your team spends manually bridging gaps between systems costing you more than the price of the tool? If the answer is yes, it's time to upgrade.
The Role of iPaaS in Your Tech Stack
Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) solutions take this whole concept to another level. Instead of just connecting two applications, they act as a central hub for your entire software ecosystem. You can think of an iPaaS as a universal translator for all your apps.
Platforms like Workato or MuleSoft let you build out incredibly sophisticated workflows visually, often using low-code or even no-code interfaces. This is a game-changer because it empowers teams outside of engineering to create their own automations.
Imagine a support manager building a workflow where a high-priority customer ticket in Zendesk automatically creates a linked "bug" issue in Jira. At the same time, it could open a new discussion thread in a specific GitHub repository for the development team to start investigating immediately. That's the kind of orchestration that defines a truly mature and integrated operational setup.
Got Questions About Your Jira GitHub Integration?
Even with a perfect plan, you're bound to hit a few snags when connecting Jira and GitHub. It happens to everyone. The good news is, most problems come down to a handful of common mix-ups with configuration or permissions.
Let's walk through the questions we hear all the time. Getting these sorted will save you a ton of headaches and get your team back to building.
Can I Connect Jira Server to GitHub Cloud?
Yes, you absolutely can. While the main app on the Atlassian Marketplace is built for Jira Cloud, there’s a different DVCS (Distributed Version Control System) connector app specifically for self-hosted Jira Server and Data Center instances.
The setup is a little different, mind you. You'll need to create an OAuth app inside your GitHub organization first, then plug those credentials into your Jira admin settings.
Here’s the one non-negotiable requirement: your Jira instance has to be accessible from the public internet. GitHub needs to send webhook updates to your server whenever a commit or pull request happens, and if it can't reach your Jira URL, the whole thing falls apart. Once that’s handled, you'll get the same rich development insights right inside your Jira issues.
What Are the Most Common Permission Errors?
Permissions are, without a doubt, the number one source of integration headaches. Nine times out of ten, the problem is that the user account used to set up the connection doesn't have the right access in GitHub.
The account you use to authenticate the app must have 'owner' or 'admin' privileges for the GitHub organization. At the very least, it needs admin rights on the specific repositories you want to connect.
If those permissions aren't there, the app can't install the webhooks it needs to listen for updates, and the integration just silently fails. On the Jira side, you also need to make sure the integration's user account can actually modify issues. Another classic mistake is adding a new private repository after the initial setup and forgetting to grant the app access to it—you often have to go in and approve each new one.
If a new private repo isn't syncing, don't just assume the integration is broken. Your first stop should always be the GitHub app's configuration page to see if it's waiting for you to grant access. That one check can save you hours of digging.
Why Aren't My Commits Showing Up in Jira?
Okay, so the integration is set up, but you're not seeing your commits, branches, or pull requests in the Jira development panel. Don't panic. There are three things to check, in this specific order.
-
Check Your Issue Key Format. This is the fix 90% of the time. A simple typo in the issue key within your commit message or branch name—like
PROJ-1234instead ofPROJ-123—is all it takes to break the connection. Double-check that it's perfect. -
Inspect the Webhook Status in GitHub. Head over to your repository’s settings in GitHub and find the "Webhooks" section. If you see a bunch of delivery errors marked with red exclamation points, that's your problem. It means GitHub is trying to talk to Jira, but isn't getting a response. This usually points to a firewall rule, a network issue, or an old Jira site URL in the app's settings.
-
Verify the Repository Configuration in Jira. If the first two checks pass, go back to the GitHub app configuration inside Jira. Make sure the repository you're working on has actually been added to the list and is enabled for syncing.
By working through these common failure points one by one, you can usually find and fix the problem in minutes. A smooth connection between Jira and GitHub is totally achievable, and it makes tracking progress a whole lot easier.
Stop letting bugs and inconsistencies in AI-generated code slow you down. kluster.ai is a real-time AI code review platform that runs directly in your IDE, catching errors before they ever become a problem. Enforce your team's standards, secure your codebase, and merge pull requests in minutes, not days. Get started for free or book a demo to see how instant verification can transform your workflow.