A Practical Guide to the Shift Left Security Approach
The shift left security approach is all about catching security issues early. Instead of waiting until the very end of a project to run a security scan—the equivalent of a last-minute panic attack—you build security into the process from day one.
It’s a simple idea with huge implications: find and fix vulnerabilities when they are cheapest and easiest to address, not when they’re already baked into your live application.
From Afterthought to Foundation

Think about building a house. What if you waited until the walls were painted and the furniture was moved in to check the foundation? Finding a crack at that stage would be a nightmare. You’d have to rip things apart, and the cost and effort would be astronomical. For years, that’s exactly how software security was handled: a final, stressful check right before shipping.
The shift left security approach flips that model on its head. The name is pretty literal. If you picture the software development lifecycle (SDLC) as a timeline from left (design, coding) to right (deployment, maintenance), security used to be stuck way over on the right. Shifting left just means pulling those security checks and balances into the earlier stages.
To really see the difference, let's compare the old way with the new.
Traditional Security vs Shift Left Security
This table breaks down how fundamentally different the two approaches are, from who owns security to when it actually happens.
| Aspect | Traditional Security (Right) | Shift Left Security (Left) |
|---|---|---|
| When it happens | At the end of the SDLC, just before deployment. | Continuously, starting from the design phase. |
| Responsibility | A separate security team (the "gatekeepers"). | A shared responsibility across developers, security, and ops. |
| Cost to fix | Extremely high. Fixing issues in production is expensive. | Very low. Fixing a bug in the IDE is trivial. |
| Process | A bottleneck. Security scans often block releases. | Integrated and automated. Security is part of the workflow. |
| Developer role | Hand off code and wait for a pass/fail report. | Empowered to write secure code with real-time feedback. |
| Speed | Slow. Creates long delays and friction. | Fast. Enables quicker, more secure releases. |
The contrast is stark. The traditional model treats security as an obstacle, while shifting left makes it a core part of building quality software.
Why This Matters
This isn’t just about tweaking a project plan; it’s a total cultural and operational shift. When you embed security into the development process, you catch problems when they’re still just a few lines of code on a developer’s screen.
This approach means adopting secure application development best practices from the very beginning, making security a habit, not a hurdle.
Shifting left transforms security from a reactive bottleneck into a proactive, collaborative effort. It’s about prevention over cure, empowering developers to build security into their work rather than having it inspected later.
Essentially, security becomes just another measure of quality, right alongside performance and functionality. When developers, security pros, and operations folks are all on the same page from the start, everyone owns the outcome.
Here are the core ideas that make it work:
- Early Detection: Finding and fixing a flaw during coding is exponentially cheaper than patching it in a live system.
- Developer Empowerment: Give developers the tools and knowledge to write secure code from the get-go. No more "throwing it over the wall" to the security team.
- Continuous Feedback: Automated security checks run right inside the developer's workflow, giving them instant alerts without slowing them down.
- Improved Collaboration: It dismantles the old silos between developers and security, creating a true DevSecOps culture where everyone works together.
Ultimately, shifting left helps you ship more resilient software, faster. You avoid the costly delays and nasty surprises that come with finding security holes at the last minute. It's about building quality in, not trying to bolt it on later.
Calculating the ROI of Shifting Security Left
So, you're sold on the concept of shifting security left. Great. But to get buy-in, you need to build a business case, and that means talking about money. The good news is, a shift-left approach delivers a compelling return on investment (ROI) that's not just theoretical.
When you move security from a reactive, last-minute fire drill to a proactive part of your workflow, you're not just adding another step. You're fundamentally changing its role from a cost center to a business enabler. Let's break down how to quantify that.
The Snowballing Cost of Bugs
The single most dramatic financial win comes from tackling the exponential cost of fixing bugs. Think of it like a leaky pipe in your house. Fix a tiny drip as soon as you spot it? A few bucks and five minutes. Wait until it floods the basement? You're looking at thousands in repairs, ruined furniture, and a massive headache.
Code vulnerabilities work the exact same way.
When a bug is just a few lines of code on a developer's screen, fixing it is trivial. It's cheap. But once that same bug gets deployed to production, the costs spiral out of control.
A landmark study by IBM found that a bug fixed during the implementation phase costs around $80. Find that same bug in production, and the price tag jumps to $7,600—that's a nearly 100x increase.
And that $7,600 isn't just developer time. A production bug triggers an all-hands-on-deck emergency. Developers, QA testers, security analysts, and Ops engineers all drop what they're doing. It means emergency patches, potential system downtime, and a frantic scramble to contain the damage before customers notice.
Direct Financial Savings
These are the hard numbers you can take straight to your CFO. Shifting left generates direct, measurable savings that easily justify the investment in new tools and training.
- Slashed Remediation Costs: This is the most immediate win. By catching flaws early, you eliminate the massive man-hour and resource drain of post-release bug fixes.
- Avoiding Breach Fines: A single data breach can cost millions in regulatory fines from laws like GDPR or CCPA, not to mention legal fees and customer payouts. Preventing just one major incident can fund your security program for years.
- Lower Cybersecurity Insurance Premiums: Insurers are getting smarter about risk. When they see you have a proactive shift left security approach, they see a lower-risk client. That often translates directly to lower premiums.
The Ripple Effect: Operational Efficiency
Beyond the direct cash savings, shifting left creates a wave of positive operational outcomes. These "softer" benefits are just as important and contribute massively to the overall ROI by making your entire engineering organization faster and more effective.
Developer Productivity Skyrockets When developers get instant security feedback right in their IDE, they can fix an issue in seconds without breaking their flow. Compare that to the old way: getting a security report weeks later and having to spend hours, or even days, digging back into old code to remember what was going on. This keeps your best people focused on building valuable features, not chasing down ghosts.
Release Cycles Get Faster Traditional security is a notorious bottleneck. How many times has a release been held up waiting for that final security sign-off? By baking security checks directly into the CI/CD pipeline, you remove that gate entirely. Teams can ship code faster and more often, with the confidence that it's already been vetted. That's a huge competitive advantage.
Customer Trust Becomes a Feature In today's market, security isn't just a backend concern—it's a product feature. A solid security reputation builds customer loyalty and protects your brand. On the flip side, one public breach can destroy years of customer trust and tank your market share.
When you combine the direct cost savings with these powerful operational gains, the value proposition becomes crystal clear. The ROI of shifting left isn't just about saving money on bug fixes; it's about building a faster, stronger, and more competitive organization from the ground up.
Your Step-by-Step Implementation Roadmap
Jumping into a shift-left security model is about more than just buying a few new tools. It’s a genuine change in how your team builds software. It demands a thoughtful, phased strategy that reworks your processes, empowers your developers, and brings in the right tech at the right time. This roadmap lays out a practical way to manage that transition.
Think of it like trying to upgrade an old car’s engine while it's still running. You can’t just rip everything out at once. You have to be methodical—replace the spark plugs, then the fuel injectors, and so on, until the whole system is modern and running smoothly. A solid shift-left implementation follows a similar, structured path.
This infographic says it all—it shows just how quickly the cost of fixing a bug skyrockets as it moves from left to right.
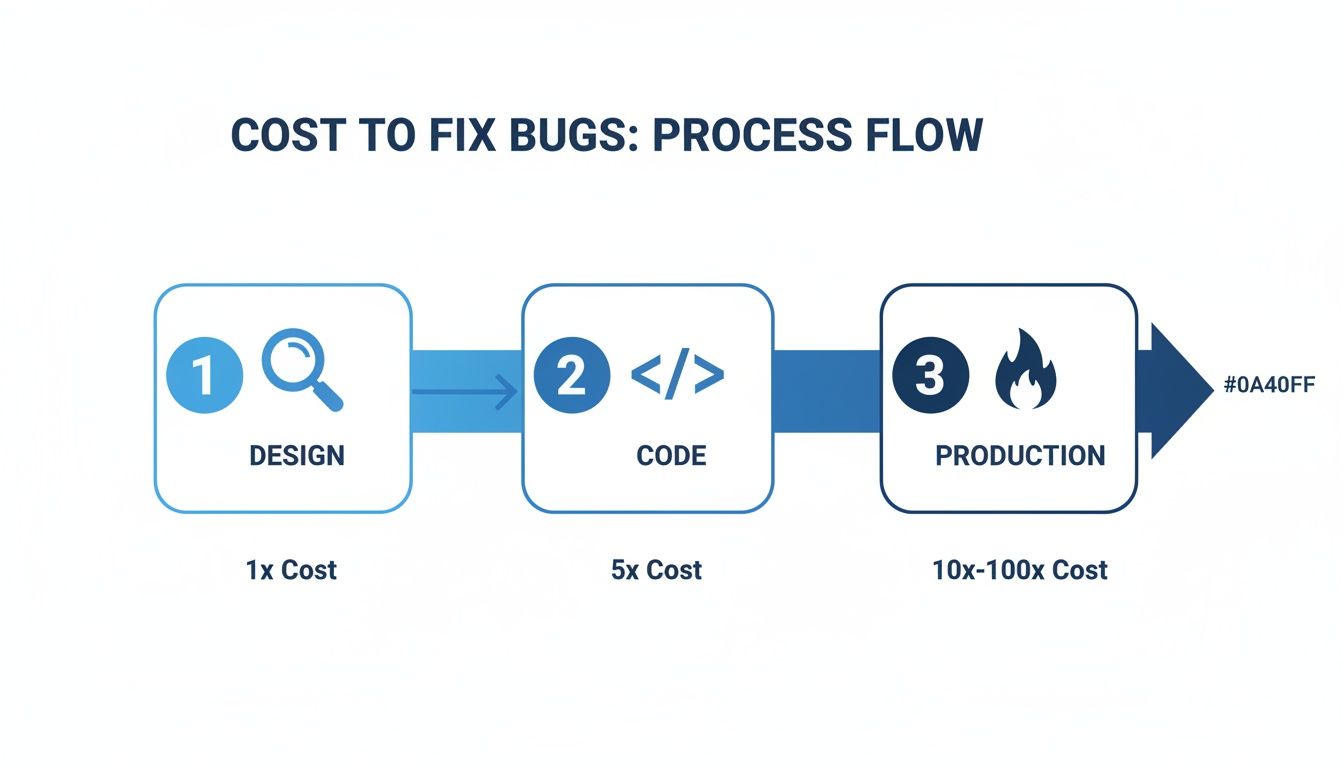
The takeaway here is brutally simple: a vulnerability that costs 1x to fix during design can balloon to over 100x that amount if it’s found in production. That financial reality is what drives the whole shift-left movement.
Phase 1: Fortifying the Foundation with Process and People
Before you even think about new technology, the first move is to get your processes and culture in line. This groundwork is non-negotiable. It ensures that when you do bring in tools, they’ll actually get used effectively instead of just adding more friction. The goal is to make security a shared, everyday responsibility, not a last-minute chore.
1. Integrate Security into Your Agile Workflows Start by making security a standard part of your development sprints.
- Add Security Stories: Treat security requirements just like you treat feature requests. Create user stories in your backlog for tasks like "implement input validation" or "update vulnerable library." This makes the work visible and plannable.
- Hold Threat Modeling Sessions: Before kicking off a new feature, run a quick threat modeling discussion during sprint planning. Ask simple questions like, "What's the worst thing someone could do with this feature?" This simple exercise gets developers thinking defensively from day one.
2. Foster a Culture of Security Ownership Your developers are your first line of defense, so you need to empower them. In fact, 70% of developers already feel it’s their job to write secure code, but many just don’t have the right training or tools to pull it off.
- Provide Role-Specific Training: Run hands-on workshops that teach secure coding practices directly relevant to your tech stack. Focus on practical skills they can use immediately, not abstract theory.
- Establish Security Champions: Find the developers on each team who are genuinely passionate about security. Give them some extra training and make them the go-to person for their peers. They become an extension of the security team, right where the code is being written.
Phase 2: Integrating Key Security Technologies
With a solid cultural and process foundation in place, you can start introducing automated tools that slot right into the developer's workflow. The trick is to pick technologies that give immediate, actionable feedback without burying everyone in alerts.
Implementing security tools isn't the end goal; it's the enabler. The true measure of success is whether these tools help developers write more secure code faster, not how many alerts they generate.
Here are the essential tool categories to wire into your CI/CD pipeline and local developer environments:
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST): These tools are like a spell-checker for security. They analyze your source code for potential vulnerabilities before it's even compiled. Modern SAST tools can give feedback right in the IDE, flagging things like SQL injection flaws as the code is being typed.
- Software Composition Analysis (SCA): Let’s be honest, your application is built on the shoulders of countless open-source libraries. SCA tools scan these dependencies for known vulnerabilities, making sure you don't accidentally inherit risk from someone else's code. This is absolutely critical, as third-party components often make up the vast majority of an application's codebase.
By layering in these technologies, you automate crucial checkpoints and give developers the instant feedback they need to conduct a much more effective security code review on their own, without ever waiting on a separate security team. This blend of process, people, and technology is what a successful shift-left security strategy is all about.
Why Most Shift Left Initiatives Fail
The idea of shifting security left is fantastic on paper. Everyone praises it, and for good reason. But in the real world, a lot of organizations stumble badly. They create this fragile illusion of security instead of building a genuinely resilient development process. They buy the scanners, check the compliance boxes, and declare victory, but the deep-seated problems that plague old-school security just reappear under a new name.
The gap between perception and reality here is staggering. A recent benchmark report found that while a whopping 82% of organizations claim their shift-left programs are a success, a tiny 4% have actually managed to clear their backlog of known vulnerabilities. That's a massive 78-point effectiveness gap—a flashing red light that something is fundamentally broken in how most teams are doing this. You can dig into the full report to see just how badly teams are struggling with container security effectiveness.
The core of the problem is simple: detection has scaled, but fixing things has not.
The Rise of Security Theater
One of the most common ways these initiatives fall apart is something I call "security theater." This is what happens when companies focus entirely on finding vulnerabilities while completely ignoring their ability to actually fix them. They invest a fortune in a suite of automated scanners—SAST, DAST, SCA—and plug them right into the CI/CD pipeline. And these tools do exactly what they promise: they find problems. A lot of them.
Suddenly, the pipeline is lit up with alerts, dashboards are bleeding red, and security teams are pumping out massive reports detailing thousands of potential issues. It looks like a robust security program. But in practice, it just creates an overwhelming flood of noise. Developers get buried under an avalanche of alerts, many of which are low-priority or just plain wrong, leading to huge backlogs that never, ever shrink.
The goal of shifting left isn't just to find every possible vulnerability; it's to fix the ones that actually matter, and fix them fast. When you're finding issues 100 times faster than you can fix them, you haven't shifted left—you've just built a more efficient way to document your technical debt.
This constant, unactionable noise just leads to a vicious cycle of frustration and burnout.
The Manual Remediation Bottleneck
While we’ve gotten incredibly good at automating detection, the process of actually fixing vulnerabilities remains a painfully manual, soul-crushing bottleneck. This, right here, is the central reason most shift-left initiatives fail. A developer gets an alert, but what happens next is a slow, frustrating mess:
- Total Context Switch: They have to stop what they're doing—building new features—and pivot to investigate some obscure security alert.
- Manual Triage: Is this even a real threat? They have to spend time validating if the vulnerability is a genuine risk or just another false positive from the scanner.
- The Research Rabbit Hole: More often than not, they have to go digging into the specific CVE, try to understand its real-world impact on their specific codebase, and then figure out the right way to patch it without breaking everything else.
- Implement and Pray: Finally, they apply the fix and run a battery of tests, hoping it works and doesn't introduce a whole new set of bugs.
This whole process is slow, wildly inefficient, and pulls developers away from their real job: building the product. When a scanner flags thousands of issues a month, but your dev team only has the bandwidth to fix a few dozen, the program is doomed from the start.
The result is crippling developer burnout—with 88% of security teams showing signs of it—and a security posture that, despite all the frantic activity, isn't getting any better. Real success means closing the loop and empowering developers to fix issues as effortlessly as the tools find them.
Using AI for a Smarter Shift Left Strategy

Real shift-left security isn't just about running scanners earlier in the pipeline. The true goal is to stop vulnerabilities from being written in the first place. That can only happen by giving developers immediate, intelligent feedback right where they work—inside their IDE. This is where AI-powered code review becomes the ultimate evolution of the shift left security approach.
Think of it like giving every developer an expert pair programmer who whispers security advice in their ear, line by line, in real time. Instead of waiting for a CI/CD build to fail minutes or hours later, developers get alerts on security flaws, logic errors, and compliance issues the second they type.
This instant feedback loop is a game-changer. It weaves security into the creative coding process, turning it from a disruptive chore into a natural part of building software.
Eliminating Noise with Context-Aware AI
We all know the story with traditional security scanners: they scream about everything. They’re notorious for a high volume of false positives because they lack context. They don't understand the developer's intent or how a piece of code fits into the bigger picture, leading to a flood of irrelevant alerts that developers quickly learn to ignore.
AI-powered tools are different because they're context-aware. A modern AI assistant analyzes not just the single line of code being written, but its relationship to the entire repository, existing documentation, and even the developer’s original prompt. This deep understanding allows the AI to provide sharp, relevant feedback, easily telling a genuine threat apart from a benign coding pattern.
By providing immediate, contextual, and actionable feedback, in-IDE AI code review eliminates the noise and friction that cause traditional shift-left initiatives to fail. It moves security from a post-coding chore to a real-time collaborative effort.
This precision is more important than ever now that AI is generating 40-60% of new code. That sheer volume can drown security teams in alerts. One analysis found it took sifting through 47 critical alerts just to find one real, exploitable vulnerability. No wonder security pros are burning out from alert fatigue. Success depends on validating real threats, not just flagging possibilities. It allows teams to shift budgets from unused scanner licenses (53% sit idle) to a smarter human-AI triage system.
Enforcing Security Gates Before the First Commit
The best in-IDE AI tools do more than just offer suggestions—they can actively enforce your organization's security policies and compliance rules before a single line of vulnerable code is ever committed. You literally can't get any more "left" than that.
- Real-Time Policy Enforcement: Configure the AI to automatically flag and block code that violates specific security standards, like using a deprecated crypto function or forgetting to sanitize inputs.
- Preventing Secret Spills: The AI can instantly detect when a developer accidentally pastes an API key, password, or other credentials into the source code, stopping a common and dangerous mistake in its tracks.
- Supply Chain Security: By integrating with Software Composition Analysis (SCA), the AI can warn a developer the moment they try to import a library with a known critical vulnerability.
This proactive enforcement turns the developer's IDE into the first and most important security gate. Issues are caught and fixed in seconds, drastically cutting down the number of vulnerabilities that ever make it to the CI/CD pipeline or a formal pull request. This approach is a core part of the broader application of AI for code, which is all about improving quality and velocity at the same time.
For anyone curious about how AI and automation are being applied across different industries, you can find more insights into Artificial Intelligence Automation. By embedding this intelligence directly into the developer's workflow, we can finally close the gap between finding a problem and fixing it, delivering on the original promise of shifting left: building more secure software, faster.
The Future of Proactive Security Management
Shifting left isn't the final destination. It's a foundational philosophy, and as organizations get better at catching vulnerabilities early, the game is already changing. The next logical step is to move beyond periodic scanning and into a state of constant vigilance. This is where Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM) comes in.
Think of CTEM as a fundamental shift in mindset. Instead of running security checks at specific gates in the pipeline, it's about having real-time visibility across your entire digital world—from code repos and cloud infrastructure to user identities and access rights. It’s about seeing the whole picture of your potential attack surface, all the time.
This next-gen strategy works by constantly pulling in data on code drift, misconfigurations, and other subtle weaknesses. By analyzing this firehose of information, security platforms can spot and prioritize risks before they ever become active threats. It lets your team proactively shrink the "blast radius" long before an attacker even gets a chance to knock on the door.
From Reactive Scans to Continuous Management
The push toward CTEM is driven by a simple, brutal reality: attackers don’t care about your scheduled scan times. As threats get more sophisticated, especially with AI-driven attacks on the rise, a reactive security posture is just no longer good enough.
You can see this playing out across the industry. Predictions show a clear move away from broad, periodic scanning. By 2026, the focus will be on replacing these intermittent checks with real-time, continuous visibility. This is absolutely critical when you consider that data exfiltration in ransomware attacks now happens over 80% of the time, making proactive defense non-negotiable. You can find more details on these cybersecurity predictions and trends on Netwitness.com.
The Foundational Role of In-IDE Tools
This is where the principles of shifting left become more critical than ever before. Real-time, in-IDE security tools are the bedrock of any mature CTEM program. Why? Because they provide the earliest possible signal of potential exposure—right at the moment a developer writes a line of code.
By flagging vulnerabilities and misconfigurations as developers type, these AI assistants feed directly into the continuous data stream that fuels a CTEM strategy. They ensure the codebase is more secure from the second it's created, drastically reducing the number of issues that ever make it out into the wider digital ecosystem.
In a CTEM world, security isn't an event that happens; it's a continuous state of awareness. In-IDE tools are the first and most immediate layer of that awareness, making developers active participants in proactive threat management.
Ultimately, the future of security is this constant, proactive management of exposure. The whole shift-left security approach, supercharged by in-IDE AI tools like kluster.ai, lays the essential groundwork for this evolution. It empowers organizations to stay ahead of threats in an environment that only gets more complex, turning security from a defensive chore into a real strategic advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Moving to a shift left security model is a big change, both culturally and technically. It's only natural to have a few questions. Let's tackle the most common ones head-on.
How Do I Get Developers On Board Without Killing Their Productivity?
This is the million-dollar question, and the answer is surprisingly simple: you have to make security an enabler, not a roadblock. Developers will actually embrace security when it’s woven directly into their daily workflow, giving them instant, helpful feedback instead of another frustrating hurdle.
Think about it. When a developer gets an alert about a potential vulnerability right as they're typing the code, they can fix it in a few seconds. That’s a world away from the pain of digging up a security report weeks later and trying to remember what that piece of code even did.
Tools that work inside the IDE make security feel less like a gatekeeper and more like a helpful co-pilot, improving the code without breaking the creative flow.
A successful shift left security strategy doesn't just add tasks; it empowers developers. By giving them tools that fit seamlessly into their workflow, security becomes a natural part of writing great code. Your developers become your first—and most powerful—line of defense.
What Are the First Steps for a Small Team?
If you're a small team, don't try to boil the ocean. The key is to start with high-impact, low-effort changes that deliver the most bang for your buck right away.
- Automate Dependency Scanning: This is your biggest win, right out of the gate. Use a free Software Composition Analysis (SCA) tool to automatically scan your open-source libraries for known vulnerabilities. It’s often the largest source of risk and the easiest to start fixing.
- Introduce Basic SAST: Integrate a lightweight Static Application Security Testing (SAST) tool into your CI/CD pipeline. Think of it as an automated first pass that catches common issues in your own code before they get any further.
- Start Simple Threat Modeling: You don't need a complex framework. Just dedicate 15 minutes during your planning meetings to ask, "What could go wrong with this new feature?" This one simple habit starts building that critical security-first mindset.
Isn't Shifting Left Just About Buying More Tools?
Absolutely not. This is probably the biggest misconception out there. While the right tools are crucial, the shift left security approach is fundamentally about changing your culture and your process. It’s about creating shared ownership of security across everyone—devs, ops, and security pros.
The strategy has to come first. You figure out what a proactive security workflow looks like for your team, then you pick the tools that automate and support it. Just buying a bunch of new scanners without changing how people work only leads to more alerts, more noise, and total burnout. It doesn't actually make you more secure.
Ready to give your developers the real-time, in-IDE security feedback they need? kluster.ai plugs directly into their workflow, catching vulnerabilities and enforcing your security policies before the code even gets saved. See how you can accelerate your shift left journey by visiting https://kluster.ai to start for free or book a demo.