A Practical Guide to Modern Secure Code Reviews
Secure code reviews are all about finding security flaws in your source code before that code makes it to production. It’s a simple concept, but it's a non-negotiable part of any modern development lifecycle.
The idea is to catch the nasty stuff—injection vulnerabilities, broken authentication, critical logic errors—as early as humanly (and automatically) possible. Doing this saves a massive amount of time, money, and stress down the line.
Why Secure Code Reviews Are a Competitive Edge

Let's get past the textbook definitions. A modern secure code review process isn't some frustrating bottleneck slowing everyone down. It's actually a powerful tool for building customer trust and protecting your revenue. Thinking of it as just another compliance checkbox is a huge missed opportunity.
When vulnerabilities inevitably slip into production, the damage goes way beyond just patching the code. You're looking at emergency hotfixes, a tarnished reputation, and a loss of customer confidence that can take years to claw back. Proactive security reviews completely flip this script, turning security from a reactive firefight into a predictable part of your workflow.
The Real-World ROI of Early Detection
The financial argument for doing this right is impossible to ignore. Finding a security flaw during the development phase costs a tiny fraction of what it costs to fix it after a breach. This isn't just about dodging fines; it's about protecting your business and keeping your developers shipping features, not fighting fires.
The data paints a pretty stark picture. The global average cost of a single data breach has now climbed to USD 4.44 million. That number is directly tied to whether or not a company has solid, secure development practices in place.
In one recent analysis, a combination of automated and manual reviews scanned 420 trillion lines of code. They found 204 million flaws and helped teams fix 131 million of them. That's millions of potential backdoors slammed shut before they could ever be exploited. If you want to dig deeper into how these reviews impact breach costs, the 2025 security trends report is a great read.
By baking security into the development lifecycle, teams can ship new features with real confidence. They know they’ve done their due diligence to minimize the risk of a costly incident. It fosters a culture where security is everyone's job, not just a problem for the security team.
Paving the Way for a Hybrid Approach
The most effective security programs don't just pick one method and stick with it. They blend the raw efficiency of automation with the irreplaceable critical thinking of a human expert.
Automated scanners are fantastic for flagging common, low-hanging fruit vulnerabilities. Think of them as your tireless first line of defense. This frees up your human reviewers to focus on what they do best: uncovering complex business logic flaws, subtle authorization issues, and architectural weaknesses that automated tools almost always miss. This guide will give you a practical roadmap for building a hybrid process that gives you the best of both worlds.
Building Your Modern Security Review Toolkit
A solid secure code review process depends entirely on the tools you build directly into your workflow. Without them, you're just staring at a mountain of code, hoping to spot vulnerabilities by hand. That’s not just slow—it’s a recipe for disaster. A modern toolkit isn’t about buying every flashy new product; it’s about layering the right scanners to create a safety net that catches things before they ever hit production.
Your first line of defense is almost always a Static Application Security Testing (SAST) tool. Think of it as a spell-checker for security flaws. SAST tools scan your source code before it's even compiled, flagging common anti-patterns like potential SQL injection points or hardcoded secrets. They're fast, run early in the pipeline, and give developers feedback almost instantly.
Integrating Dynamic and Real-Time Scanners
But SAST can't see everything. It has no idea how your application actually behaves once it's up and running. That’s where Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) tools come into play. A DAST scanner tests your live application from the outside, poking and prodding it just like an attacker would. This is perfect for catching server misconfigurations and runtime vulnerabilities that static analysis is blind to.
The most developer-friendly tools, though, are the ones that provide feedback in real-time. Left Shift Application Security Testing (LSAST) tools and AI-powered code assistants live right inside a developer's IDE. They flag potential security flaws and offer suggestions as the code is being written. This immediate feedback loop is incredibly powerful for preventing vulnerabilities from ever being committed in the first place. You can learn more about how this works by automating your code review process.
The goal is to make security a natural part of writing code, not some separate, painful step tacked on at the end. When feedback is instant and contextual, developers start writing secure code by habit.
The Rise of AI-Powered Review Partners
AI assistants are quickly becoming a non-negotiable part of the review process. They can instantly spot common mistakes, suggest more secure alternatives, and even explain why something is a vulnerability. It’s like having a security expert sitting next to every developer, which not only speeds up reviews but also acts as a continuous training tool for the whole team.
The numbers back this up. The market for secure code review tools is on track to hit USD 2.46 billion by 2033. This isn't just hype; it's a direct response to the explosion in disclosed vulnerabilities, with projections nearing 50,000 CVEs for this year alone. That sheer volume makes automated help an absolute necessity. For a deeper dive into these numbers, you can explore the full market research.
To help you choose the right tools, let's break down the main types of scanners and where they fit in your workflow.
Comparing Security Scanning Tool Types
| Tool Type | What It Scans | Best For | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAST | Source Code & Binaries | Finding bugs early in the SDLC, before runtime. | A developer commits code, and a pre-commit hook runs a SAST scan to check for hardcoded API keys. |
| DAST | Running Applications | Identifying runtime vulnerabilities and server misconfigurations. | Running a scan against your staging environment to find open ports or XSS vulnerabilities. |
| LSAST/AI | Code in the IDE | Providing instant feedback to developers as they type. | An AI assistant flags a risky function call in VS Code and suggests a safer alternative on the spot. |
| SCA | Dependencies & Libraries | Finding known vulnerabilities in third-party code. | A CI/CD pipeline fails because a newly added npm package has a known critical CVE. |
By combining SAST for pre-build checks, DAST for runtime analysis, and in-IDE AI assistants for real-time feedback, you build a multi-layered defense. Each tool has its own strengths, and using them together gives you far better coverage than relying on any single solution.
Designing a Hybrid Review Process That Works
Look, the best secure code review programs don't make you choose between fast automation and sharp human insight—they blend them. A smart hybrid model uses machines for the grunt work, freeing up your experts to hunt down the complex, high-impact bugs that really matter.
The first step is to embed automated security scanners right into your CI/CD pipeline. The goal is to make these scans a non-negotiable part of every single pull request. This creates an instant first line of defense, catching the common, well-known stuff like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and outdated dependencies before a human ever lays eyes on the code.
Think of this first pass as a powerful filter. Instead of your senior engineers wasting time on repetitive findings, they get a pre-vetted codebase. The automated scan report becomes their starting point, letting them skip the noise and zero in on the areas that actually need a brain.
Empowering Human Expertise
With the low-hanging fruit cleared out, your human reviewers can focus on the subtle but severe flaws that automated tools almost always miss. These are often vulnerabilities tied directly to your specific business logic—things a generic scanner can't possibly understand.
This is where manual secure code reviews truly shine. A person can ask critical questions a machine simply can't:
- Authorization Flaws: Does this new API endpoint just check if a user is logged in, or does it correctly verify they're allowed to access this specific resource?
- Business Logic Bypasses: Could someone manipulate this checkout process to apply a discount twice? Or maybe skip a payment step entirely?
- Race Conditions: What happens if two users try to grab this shared resource at the exact same millisecond?
This visual shows how different tools can work together, creating a security safety net at multiple points in your development process.
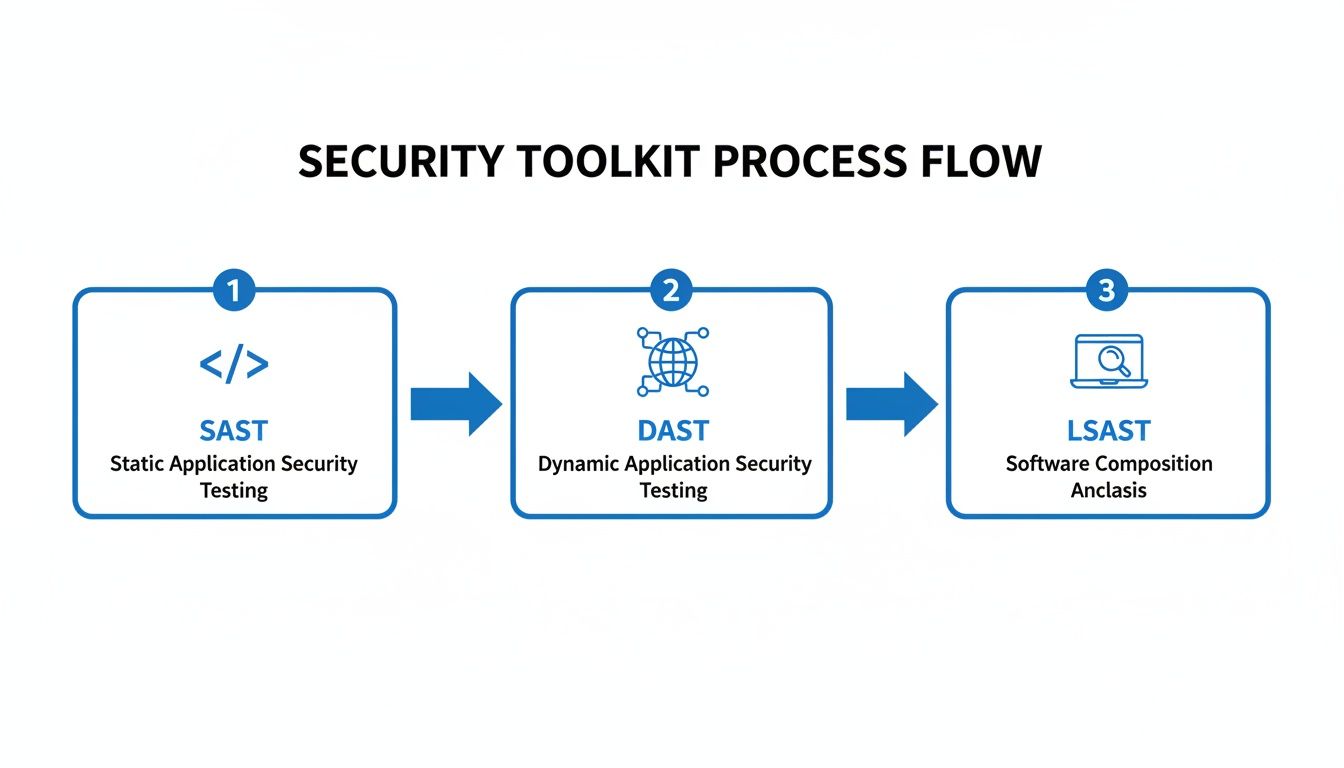
This layered approach—from static code analysis all the way to in-IDE feedback—ensures security isn't just an afterthought tacked on at the end.
Building a Practical Hybrid Workflow
Let’s be real: relying only on human reviewers for everything isn't just slow, it's a recipe for failure. Human attention has well-documented limits. Research shows a reviewer’s effectiveness craters after inspecting just 80–100 lines of code. It could take up to 14 separate reviewers to hit 95% confidence in finding all defects. If you want to go deeper on this, you can read the full analysis on AI code review tools.
This is exactly why a hybrid model is essential. By automating the mundane, you save your team's cognitive energy for the complex logic and design flaws that pose the greatest risk.
To put this into practice, you can set up specific merge checks or gating policies in your version control system. A common—and highly effective—setup is a two-part requirement for merging any critical code:
- A Clean Automated Scan: The pull request must pass all configured SAST and dependency checks without introducing any new critical or high-severity vulnerabilities.
- A Human Sign-Off: The code must be approved by at least one other developer or a designated security champion.
This dual-key system ensures both speed and depth are baked into your quality gate. It provides a baseline of automated assurance while guaranteeing that a human has considered the context, intent, and potential business logic holes in the change. This balanced approach is the bedrock of a mature and practical secure code review process.
An Actionable Checklist for Manual Security Reviews

Automated scanners are great for catching the low-hanging fruit and common anti-patterns. But they can’t grasp business context, which is where the most dangerous vulnerabilities hide. This is where a human reviewer, armed with a solid checklist, becomes the most important part of any real secure code reviews program.
A manual review isn’t about double-checking what a scanner already flagged. It’s about hunting for the subtle, context-dependent flaws that lead to major breaches. Think of it as the difference between spell-checking a document and editing it for clarity and meaning. The machine handles the syntax; the human ensures the logic is sound. This checklist is a starting point for your team, focusing on the high-impact areas where human intuition is irreplaceable.
Scrutinizing Authentication and Authorization
This is ground zero for critical vulnerabilities. Authentication is all about verifying who a user is, while authorization confirms what they’re allowed to do. Automated tools often see these as the same thing, leaving massive security gaps.
When you're reviewing, get specific with these questions:
- Is authorization enforced on the backend for every action? A classic rookie mistake is just hiding a button on the front end. Every single sensitive API endpoint must re-verify that the authenticated user has the right permissions for that specific resource and action.
- Are user roles checked correctly? Be on the lookout for hardcoded role checks (e.g.,
if user.role == 'admin'). These are brittle and risky. Is there any path for a user to escalate their own privileges? - How are session tokens managed? Are they securely stored? Do they expire properly? And critically, are they invalidated on logout?
A depressingly common failure is the Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR) vulnerability. This is when an endpoint like
/api/orders/123only checks if the user is logged in, not if they actually own order #123. A human reviewer can spot this logic flaw in seconds.
To help focus your manual reviews, here are some of the most critical vulnerabilities that often slip past automated tools.
Top 5 Vulnerability Checks for Manual Review
| Vulnerability Class | Key Question | Common Mistake |
|---|---|---|
| Authentication | Are password reset flows secure against token leakage or enumeration? | Sending reset tokens in URL parameters or providing different responses for existing vs. non-existing users. |
| Authorization | Does this API endpoint check ownership of the resource, not just user role? | A user can access /users/456/profile even though they are user #123. |
| Input Validation | Is user-supplied data being used to build file paths or system commands? | Directly concatenating a user-provided filename into a path, leading to Path Traversal attacks. |
| Business Logic | Can a user manipulate the order of operations to bypass a check? | Completing a purchase with a negative quantity to get a refund or submitting a form twice before the server can update a state. |
| Configuration | Are verbose error messages or stack traces disabled in production? | An exception reveals internal paths, library versions, or database table names to an attacker. |
Asking these kinds of pointed, context-aware questions is what makes a manual review so valuable.
Validating All User-Controlled Input
You have to assume that every piece of data coming from a user or another system is hostile. This isn't just about form fields—it includes URL parameters, headers, cookies, and especially file uploads. Treat all incoming data as untrusted until you've proven otherwise.
- Hunt for Injection Flaws: Scrutinize any code where user input is glued into database queries (SQL injection), shell commands (command injection), or HTML (XSS). The only acceptable solution is using parameterized queries and proper output encoding. No exceptions.
- Check Type, Format, and Length: Make sure the application is strict about what it accepts. If you expect an integer, don't accept a string. If the username can only be 20 characters, enforce it. This simple validation shuts down a whole class of attacks.
To see how these checks fit into a bigger picture, your code-level reviews should be part of a comprehensive cyber security audit checklist. This connects your development practices to the organization's overall security posture.
Reviewing Dependencies and Configuration
Your code doesn't live in a bubble. It runs on a stack of third-party libraries in a configured environment, and both can be sources of serious vulnerabilities.
A manual review is perfect for verifying that dependencies are actively maintained and free from known critical vulnerabilities. Even more important, sniff out hardcoded secrets like API keys or database passwords. These should never be in the source code. They belong in a secure vault or environment variables, loaded at runtime.
Adding this check is easy. You can see how these steps fit into a larger quality gate by exploring our detailed pull request checklist.
How to Measure and Improve Your Security Program
A secure code review program is only as good as the results it delivers. Without clear metrics, you're just guessing. You might feel busy, but are you actually making the codebase safer?
Tracking the right data is what separates a genuine security program from security theater. It turns what feels like a cost center into a proven value driver, giving you the hard evidence needed to justify resources and push for real improvements. The key is to stop focusing on vanity metrics like "bugs found." That number is meaningless on its own.
Instead, we need to track metrics that tell a story about efficiency, risk reduction, and developer behavior. This data isn't for shaming developers; it's for spotting patterns, identifying where we need better training, and showing leadership that our efforts are paying off.
Key Metrics for Your Security Dashboard
To get started, you don't need a dozen different charts. A handful of core metrics can give you a surprisingly clear snapshot of your program's health. These are the numbers that resonate with everyone, from the engineering team on the ground to the stakeholders in the boardroom.
- Mean Time to Remediate (MTTR): This is the big one. How long, on average, does it take a developer to fix a security bug after it's been identified? A falling MTTR is a fantastic sign that your process is getting smoother and developers are getting faster at squashing vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability Recurrence Rate: What percentage of bugs that you've already fixed manage to creep back into the codebase? If this number is high, it’s a red flag. It might mean developers didn't understand the root cause of the original flaw, or maybe your regression tests are missing something important.
- Flaw Density: This is usually measured as the number of vulnerabilities per one thousand lines of code (KLOC). Tracking this over time helps you see if new code is being written more securely from the start.
The most powerful metrics are the ones that connect security directly to development velocity and risk. A low MTTR and a near-zero recurrence rate prove your team isn't just shipping code—you're shipping safer code, faster, without kicking the can down the road.
Turning Data into Actionable Insights
Collecting this data is just the first step. The real magic happens when you use these numbers to make strategic decisions. This is where you go from just reporting to actively improving.
For example, let's say you notice one team consistently has a high flaw density, and most of their bugs are related to SQL injection. That's not a reason to blame them. It's a clear signal that they need targeted training on input validation and parameterized queries. Problem solved.
Or maybe you see your overall MTTR starting to creep up. This could mean developers are getting stuck. Are the findings from your security scanners confusing? Is the remediation advice unclear? This is your cue to improve the documentation or offer more hands-on support during the secure code reviews.
Ultimately, your metrics should tell a story that fits into the bigger picture of your company's Secure Software Development Lifecycle. When you can show that you're strengthening every stage—from design to deployment—you’re no longer just talking about security. You're demonstrating a clear return on investment.
Common Questions About Secure Code Reviews
Even with the best tools and checklists, shifting to a security-first culture is going to bring up some real-world friction. Teams almost always run into the same hurdles, from developers feeling blocked to honest uncertainty about what to prioritize.
Getting ahead of these questions is the key to making your secure code reviews program actually stick.
How Do We Handle Developer Pushback?
This is probably the most common concern, and it's a fair one. Engineers might see these new steps as just another bottleneck slowing down velocity. The trick is to reframe the whole process. This isn't a gate; it's a guardrail designed to help them ship with more confidence.
The best way to do that is to make security as frictionless as you can. Don't just flag problems—make sure your tools and human reviewers provide clear, actionable advice on how to fix them. You have to explain the "why" behind a finding. When a developer understands the potential impact of a vulnerability, they're far more likely to buy into fixing it.
It's all about collaboration over criticism. A secure code review should feel like a partnership, not an audit. Celebrate the wins, and give a shout-out to engineers who consistently write secure code. That kind of positive reinforcement helps build a culture where security is a shared responsibility, not just another task to check off.
A common pitfall is treating a security finding like a personal critique. Frame it as a collective learning opportunity instead. When a new type of vulnerability pops up, turn it into a quick team-wide lesson so everyone learns how to spot it next time.
Are Automated Scanners Enough on Their Own?
We hear this one a lot, and the answer is a hard no. Don't get me wrong, automated SAST and DAST tools are essential. They're great for catching the low-hanging fruit—the common, known vulnerabilities. But they are completely blind to business logic flaws.
An automated scanner has no idea if your authorization model is broken or if a multi-step checkout process can be manipulated to get a product for free.
Think of it this way:
- Automation finds the typos. It’s fantastic at spotting things like a potential SQL injection or an outdated library.
- Humans find the plot holes. You need a person to understand the application's context and identify flaws in the underlying logic that an attacker could exploit.
Relying only on automation creates a dangerous false sense of security. The most damaging breaches often come from exploiting these complex, context-specific vulnerabilities that only a human reviewer can catch. A hybrid approach, combining the speed of automation with the critical thinking of a manual review, is the only way to build a defense that actually holds up.
Ready to eliminate security vulnerabilities before they ever leave the editor? kluster.ai integrates directly into your IDE, providing real-time, AI-powered secure code reviews that catch flaws instantly. Start free or book a demo at https://kluster.ai to enforce security policies and ship trusted code faster.